The Great London:
Cultural Heritage
UK: 'Unique' Roman tombstone found in Cirencester

UK: New light for old master paintings

UK: 76 skeletons discovered at Saxon Woolwich

UK: 500-year-old English Bible reveals Reformation secrets

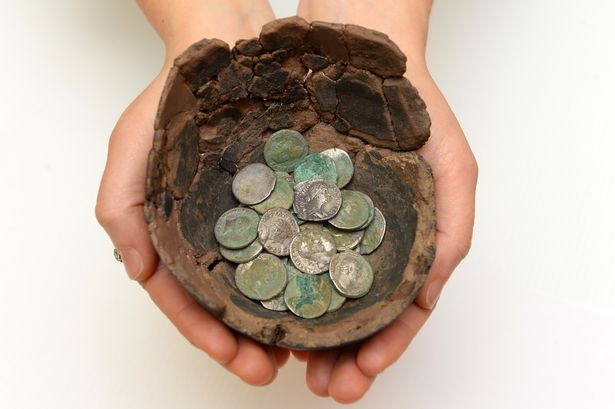
UK: Roman coins issued by Mark Antony found in Welsh field

UK: 1,967 bodies exhumed at Georgian-era cemetery in UK

UK: Tudor church graffiti records names of plague victims

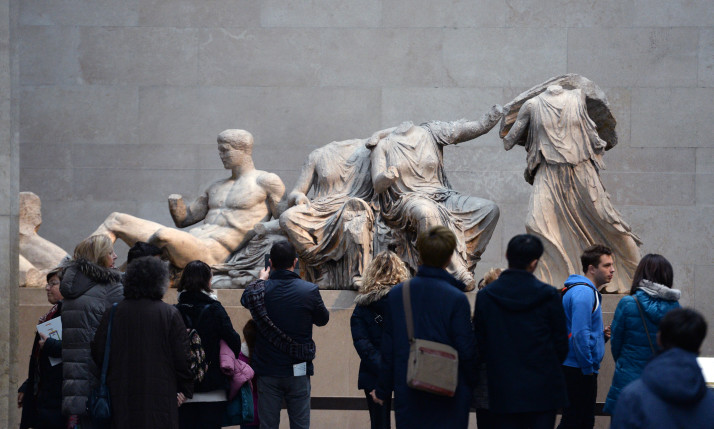
United Kingdom: Britain urged to begin talks on Parthenon marbles

UK: Tiny Tudor treasure hoard found in Thames mud

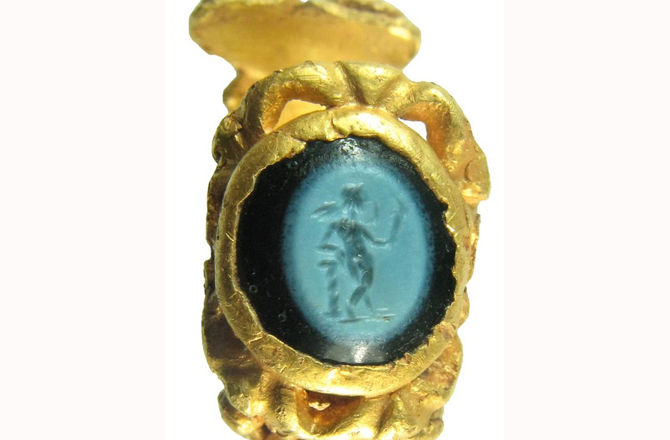
UK: Roman gold ring depicting Cupid found in UK

UK: Archaeologists search for Roman remains in Gloucester

France: 6,000-yr-old skeletons in French pit were victims of violence

Breaking News: Neanderthals killed off by diseases from modern humans, claims study

UK: The culinary habits of the Stonehenge builders

Forensics: Five things you can learn from a Roman skeleton

UK: Stonehenge's bluestones moved by glaciers

United Kingdom: Athenians’ association sues Britain for Parthenon Sculptures

Natural Heritage: Epoch-defining study pinpoints when humans came to dominate planet Earth
Genetics: Scientists sequence ancient British 'gladiator' genomes from Roman York

Iraq: Reports of third ancient site looted by IS militants
