The Great London:
ecology
Natural Heritage: Sampling species' DNA trails is leading to better environmental monitoring

Oceans: Chemicals threaten Europe's killer whales with extinction

Natural Heritage: Epoch-defining study pinpoints when humans came to dominate planet Earth
Indigenous Cultures: Brazil land grab threatens isolated tribes: activists

Environment: Kew report urges global scientific community to secure health of the planet

Natural Heritage: Bitter chocolate: Illegal cocoa farms threaten Ivory Coast primates

Oceans: First evidence of deep-sea animals ingesting microplastics
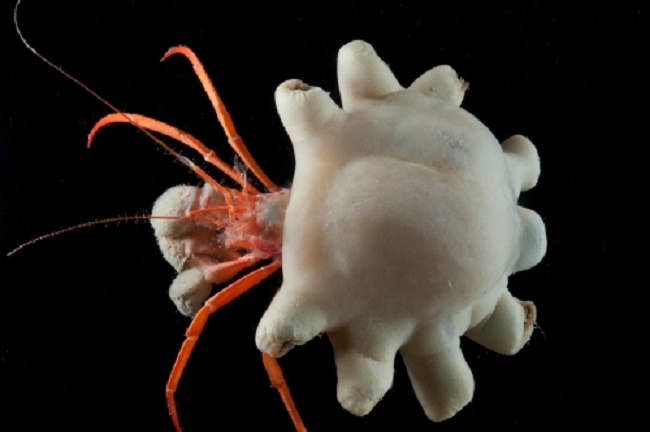
Ecosystems: Humans artificially drive evolution of new species

Natural Heritage: Effects of past tropical deforestation will be felt for years to come

Environment: Wetlands and agriculture, not fossil fuels could be causing a global rise in methane

Natural Heritage: Scientists warn only 'simplified', degraded tropical forest may remain by end of century
